| Section | Summary |
|---|---|
| Understanding the Core Principles of Halal Food Standards | Insight into central prohibitions, humane animal treatment, ethical slaughter practices, cross-contamination avoidance, transparent labeling, verification by credible bodies, and continuous compliance monitoring under Halal food standards. |
| Overview of Various Halal Food Standards | Examination of Halal food standards by various certifying bodies across different regions, like IFANCA in the USA, HFA in the UK, MUI Halal in Indonesia, JAKIM Halal in Malaysia, and ESMA Halal in UAE, each reflecting regional regulatory frameworks alongside Islamic dietary principles. |
| Factors to Consider When Selecting a Halal Food Standard | Guidance on choosing the right Halal standard considering market access, credibility of certifying body, compliance requirements, cost implications, support and guidance, feedback from peers, and long-term strategic fit. |
| Seeking Expert Guidance | Highlighting the need for professional guidance to navigate the intricacies of Halal certification, mentioning companies like Mars Quality for Halal Audit services. |
| Conclusion | Discussion on the commitment and opportunity in embarking on the Halal certification journey, emphasizing the choice of Halal standard as a pivotal decision for success. |
Embarking on the journey of Halal certification opens a gateway to a market of over 1.8 billion consumers worldwide. The Islamic dietary laws are precise, and adhering to them is not just about compliance but an embodiment of trust and quality assurance to the consumers. As the global marketplace burgeons with diverse food choices, the demand for Halal certified products is on a steep rise. This surge is not confined to Muslim-majority countries but is notable across the globe, underlining the universal appeal of Halal-certified products. The essence of Halal food standards transcends beyond the religious adherence, marking a territory of quality and safety. However, the landscape of Halal food standards is as diverse as the Muslim communities around the globe. There’s a myriad of standards, each with its nuances tailored to the regional interpretations of Islamic dietary laws. As an entity eyeing the Halal market, understanding these standards, their similarities, and their differences is the cornerstone of a successful Halal certification journey.
1. Understanding the Core Principles of Halal Food Standards
Here’s a glimpse into these core principles that form the basis of various Halal food standards worldwide:
- Prohibition of Specific Substances:
- Central to Halal food standards is the prohibition of certain substances, including pork and its by-products, and any form of intoxicants including alcohol. These prohibitions are non-negotiable and form the bedrock of all Halal certifications.
- Humane Treatment of Animals:
- The humane treatment of animals is a quintessential aspect of Halal food standards. This includes providing a good life, a good end, and ensuring the health of the animal at the time of slaughter.
- Ethical Slaughter Practices:
- Halal food standards necessitate that the slaughtering process adheres to Islamic rites, which include reciting a prayer at the time of slaughter and ensuring that the blood is fully drained from the veins.
- Avoidance of Cross-Contamination:
- Ensuring that Halal-certified products are free from cross-contamination with non-Halal substances is imperative. This extends to the entire supply chain process including storage, transportation, and handling.
- Transparent Labeling and Traceability:
- Halal food standards emphasize the importance of clear labeling and traceability to ensure that consumers are well-informed about the products they purchase.
- Verification and Certification by Credible Bodies:
- Obtaining Halal certification from reputable and recognized bodies is a critical step to gain trust and market access.
- Continuous Compliance Monitoring:
- Adherence to Halal standards is not a one-time event but a continual process. Regular audits and reviews are part and parcel of ensuring sustained compliance.
These core principles underscores the meticulous care and ethical considerations embedded within Halal food practices, reflecting a holistic approach to food safety and quality that resonates well beyond the Muslim community.
2. Overview of Various Halal Food Standards
Across the globe, the fabric of Halal food standards is as diverse as the tapestry of cultures that embody the Islamic faith. Various countries and regions have established their own Halal certifying bodies, each with a unique set of standards tailored to the local context while adhering to the core principles of Halal. Here’s a glimpse into some prominent Halal food standards from different corners of the world:
- Islamic Food and Nutrition Council of America (IFANCA): The IFANCA oversees Halal certification in the USA, ensuring that products comply with Islamic dietary laws while also meeting the stringent quality and safety standards required by American regulatory bodies.
- Halal Food Authority (HFA) – UK: Operating in the United Kingdom, the HFA is dedicated to ensuring that the Halal products available in the market are genuinely compliant with Islamic Sharia law and the regulations of the land.
- MUI Halal – Indonesia: The Indonesian Ulema Council (MUI) is the authoritative body that certifies Halal products in Indonesia, which has the largest Muslim population globally. Their certification process is robust, reflecting the country’s rich Islamic heritage.
- JAKIM Halal – Malaysia: The Department of Islamic Development Malaysia (JAKIM) is the official Halal certification body in Malaysia, known for its rigorous standards and thorough certification process, making it highly respected both domestically and internationally.
- ESMA Halal – UAE: The Emirates Authority for Standardization and Metrology (ESMA) administers Halal certification in the UAE, ensuring that products align with both Islamic dietary laws and the high-quality standards expected in the Emirates.
Each of these certifying bodies has developed standards that reflect a harmonious blend of Islamic dietary principles and the regional regulatory framework. They serve as gatekeepers of Halal integrity, ensuring that consumers can confidently choose Halal products that meet their religious, ethical, and quality expectations.
3. Factors to Consider When Selecting a Halal Food Standard
Choosing the right Halal standard for your business is a strategic decision that requires a nuanced understanding of various factors. Here are some critical considerations to guide your selection process:
- Market Access: Consider the market access that a particular Halal certification will provide. Some certifications are more widely recognized and accepted, thus opening up broader market opportunities.
- Credibility and Recognition of the Certifying Body: Opt for Halal certifying bodies that are well-recognized and have a solid reputation for maintaining high standards of Halal certification.
- Compliance Requirements: Assess the compliance requirements of different Halal standards and evaluate how well they align with your existing operations and quality management systems.
- Cost Implications: Evaluate the cost implications of adhering to a particular Halal standard, including the certification fee, compliance costs, and any necessary adjustments to your operational processes.
- Support and Guidance: Look for certifying bodies that provide adequate support, guidance, and resources to help you navigate the certification process smoothly.
- Feedback from Peers: Seek feedback from industry peers who have undergone Halal certification. Their experiences could provide valuable insights into the process and the benefits of different Halal standards.
- Long-term Strategic Fit: Evaluate how the chosen Halal standard aligns with your long-term business strategy and growth objectives.
Weighing these factors carefully will provide a clear roadmap towards selecting a Halal standard that not only fulfills the religious compliance but also aligns well with your business goals, ensuring a mutually beneficial engagement with the Halal market.
4. Seeking Expert Guidance
Navigating the intricacies of Halal certification necessitates a blend of religious understanding, legal acumen, and operational expertise. It’s a terrain where professional guidance can spell the difference between smooth sailing and turbulent waters. Here’s where companies offering Halal Audit services like Mars Quality come into play:
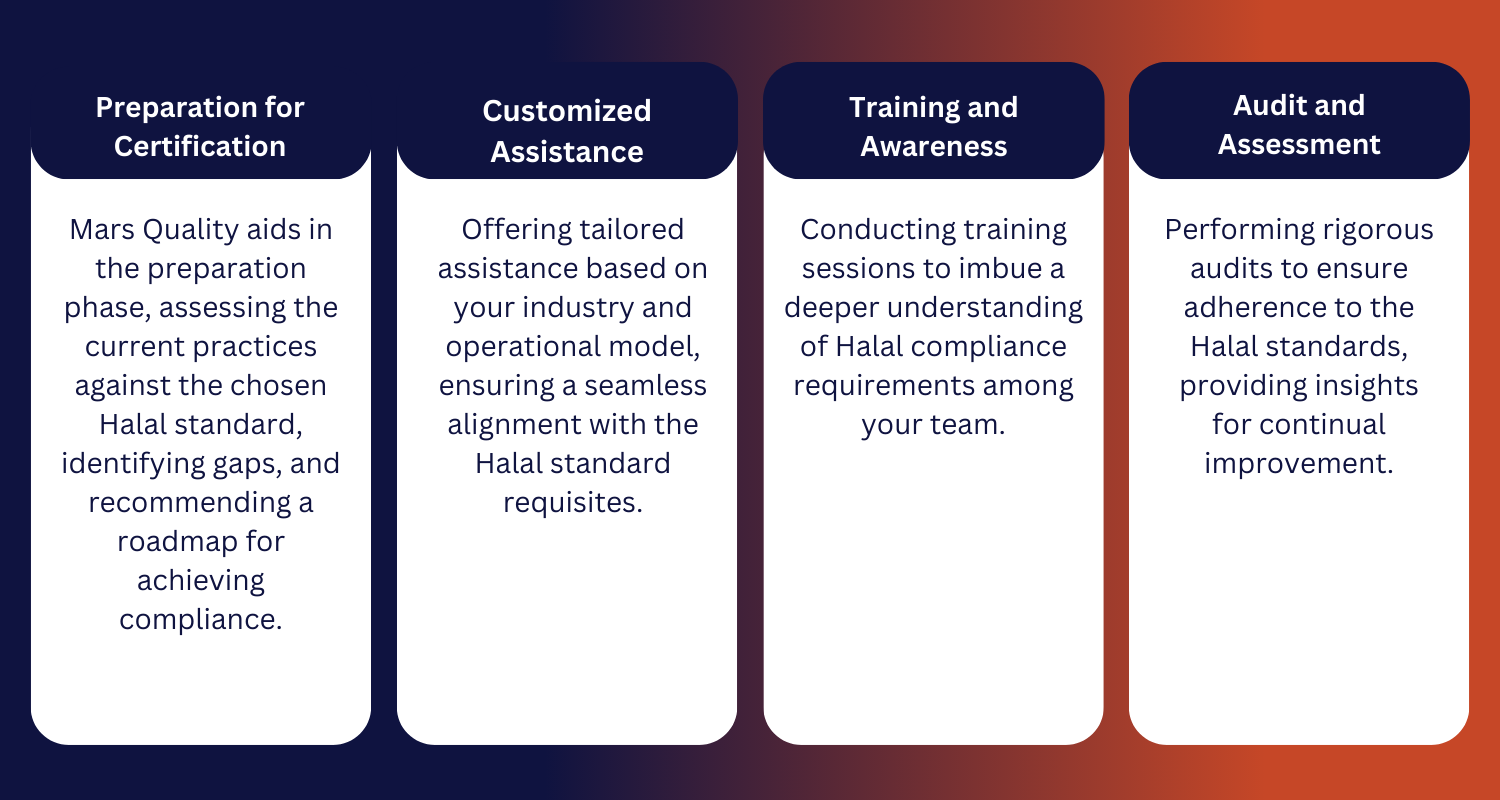
The expertise and support from seasoned professionals streamline the journey towards Halal certification, ensuring it’s not just a tick-box exercise but a value-driven endeavor.
5. Conclusion
The voyage towards Halal certification is both a commitment and an opportunity. It’s a commitment to uphold the ethical and quality standards as dictated by Islamic dietary laws. Simultaneously, it’s an opportunity to tap into a burgeoning market, build a reputable brand, and foster a culture of excellence within your organization. The choice of Halal standard is a pivotal decision on this voyage. It requires a well-thought-out strategy, understanding of the market dynamics, and expert guidance to navigate the complex landscape of Halal certification. With a conducive Halal standard and the right guidance, the horizon is broad and promising for enterprises ready to embark on this rewarding journey.

